MANE 6313
Week 4, Module G
Student Learning Outcome
Analyze simple comparative experiments and experiments with a single factor.
Module Learning Outcome
Evaluate the Box-Cox Transformation for non-homoskedastic data.
Resources for the Week 4, Module G micro-lecture are:
Box-Cox Method
- Power transformation used to stabilize variance
\[
y^*=y^\lambda
\]
- Computational formula
\[
y^{(\lambda)}=\left\{ \begin{array}{cc}\frac{y^\lambda-1}{\lambda\dot{y}^{\lambda-1}} & \lambda\neq 0\\ \dot{y}\ln y & \lambda=0 \end{array}\right.
\]
- Note \(\dot{y}\) is the geometric mean and is computed by using
\[
\dot{y}=\ln^{-1}\left[\frac{\sum\ln y}{n}\right]
\]
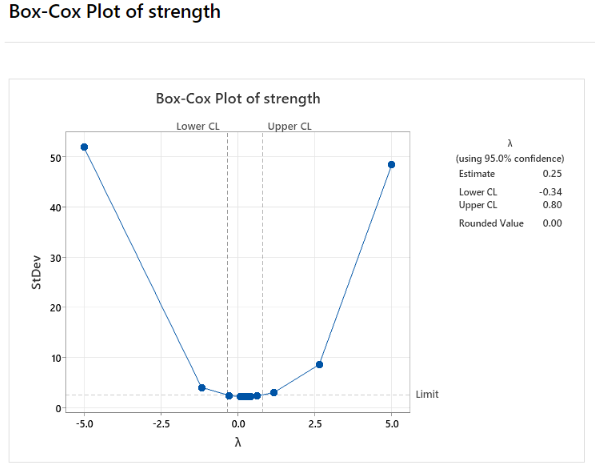
Selecting Value of Lambda
- Plot \(\lambda\) versus \(SS_E\left(\lambda\right)\)
- Recommends to select simple values 0.5 versus 0.58 even though 0.58 is optimal
Minitab Output
Minitab Demonstration
- Minitab: estimate \(\lambda\)
- Minitab: Box-Cox Transformation
- Minitab: Before/After Comparison